All-In-One Scriptless Test Automation Solution!
All-In-One Scriptless Test Automation Solution!
Top 3 CTO Approaches for Cloud Migration and Modernization Using Microservices Focused DevOps with Continous Testing
Cloud migration and data modernization requires a DevOps approach that revolves around Microservices. This means organizing teams around the capabilities of the business and domain logic instead of a specific technology stack. While we often come across teams that are UI based or Middleware based or Database based, our DevOps Teams are delivery centred and focused around specific Microservices.
Find Answers to Some Key Questions
When do CTOs Use Application Encapsulation as a Modernization Strategy?
When do CTOs Use Application Rehosting as a Modernization Strategy?
When do CTOs Use Application Replatforming as a Modernization Strategy?
What are the Key Steps Involved in Refactoring and Rearchitecting Code?
To enable a culture of Continous Integration DevOps teams must possess hands-on expertise in using tools such as GitHub for source collaboration, Atlassian for issue tracking, or using Jenkins for build version tracking. However, to speed up the rate of delivery and continuous innovation, an API-First strategy and expertise can be the gamechanger that your team needs.
Discover how we use our expertise for running sprints to decouple components, identify reusable components (Databases & Codes) to build Miicroservices API, Test the APIs, and launch new releases using time-bound sprints.
Our Legacy Integration specialists will not only identify the right data pipelines, but also speed-up the launch of new functionalities using No-Code API plugins.
1. Encapsulation: Leverage and extend the application features by encapsulating its data and functions, making them available as services via an API.
By encapsulating data and functions related to personal financial management and peer-to-peer payments, a Bank’s services can be enhanced by extending delivery through digital banking applications while maintaining modularity, scalability, and efficiency.
This approach ensures that the application remains flexible and adaptable to future enhancements and regulatory requirements, ultimately delivering greater value to its customers.
Use Case: Extending Digital Banking Application Features
Current State:
Digital Banking Application: Provides basic functionalities like account management, funds transfer, and bill payment.
Data Model: User, Account, Transaction.
Goal:
Extend Features: Introduce personal financial management tools and peer-to-peer payments.
Encapsulation: Organize data and functions related to new features separately from existing ones.
2. Rehosting: Redeploy the application component to other infrastructure (physical, virtual or cloud) without modifying its code, features or functions.
By redeploying application component to a hybrid infrastructure, the bank gains the ability to leverage cloud resources for scaling applications horizontally and vertically. Redundancy across on-premises and cloud environments enhances application resilience and fault tolerance.
The Hybrid infrastructure allows the bank to optimize costs by leveraging on-premises resources for stable workloads. The bank retains the flexibility to adapt to changing business requirements and regulatory constraints without significant architectural changes.
Use Case: Redeploying Banking Application to Hybrid Infrastructure
Current State:
Banking Application: Hosted on-premises, serving customers with basic banking functionalities.
Monolithic Architecture: All components of the application are deployed together on physical servers.
Goal:
Hybrid Infrastructure: Redeploy the banking application to a hybrid infrastructure consisting of on-premises servers and cloud services.
No Code Changes: Ensure that the existing codebase, features, and functions remain unchanged.
3. Replatforming: Migrate to a new runtime platform, making minimal changes to the code, but not the code structure, features or functions.
By migrating its banking application to a new runtime platform, the banking application can leverage auto-scaling capabilities to handle fluctuating user demand more efficiently. It Re-platforming through containerization and cloud-native architectures can result in faster deployment times and better resource utilization. Containerized applications are easier to maintain and update, leading to reduced downtime and faster time-to-market for new features. It also offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing the bank to optimize costs based on actual usage.
Use Case: Migrating Banking Application to a New Runtime Platform
Current State:
Banking Application: Monolithic architecture, deployed on traditional servers.
Legacy Runtime Platform: Aging infrastructure with limited scalability and performance.
Goal:
New Runtime Platform: Migrate the banking application to a modern, cloud-native runtime platform.
Minimal Code Changes: Ensure that existing codebase, features, and functions remain largely unchanged.
Key Steps Involved in Refactoring and Rearchitecting Code of Monolithic Systems
Code Review and Analysis:
Refactoring:
Performance Optimization:
Decomposition into Microservices:
Integration of Modern Technologies:
Automated Testing and Quality Assurance:
Documentation and Knowledge Sharing:
Read More Case Studies on Continous Testing and Banking Domain Focused DevOps Practice
A top Federal Bank has used our DevOps expertise to speed-up the process of restructuring and optimizing existing banking application codebase. The client is now able to address accumulated technical debt and improve nonfunctional attributes such as performance, scalability, reliability, and maintainability.
Our approach to reusable codes and Microservices focused DevOps ensures that the application remains robust, efficient, and adaptable to evolving business requirements and technological advancements in the banking industry. With a modernized codebase, the Bank’s Credit Union is able to deliver a superior banking experience to its members while reducing operational costs and mitigating risks associated with the legacy system.
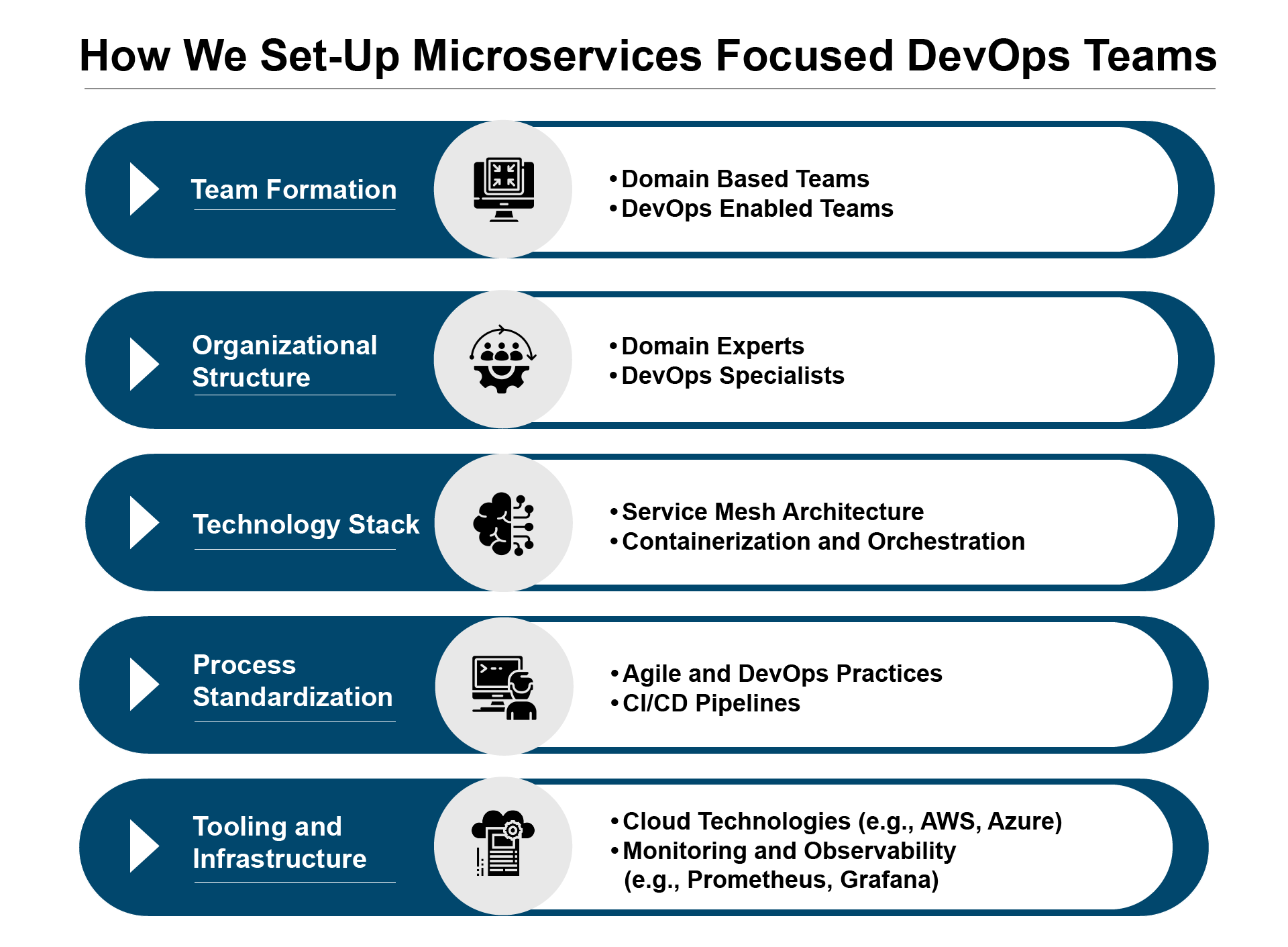
Scenario 1: Retail Banking Platform Modernization
Objective: The CTO of a large retail banking operations team aims to modernize its legacy banking platform to enhance agility, scalability, and customer experience.
Team Formation:
Organizational Structure:
Technology Stack:
Process Standardization:
Tooling and Infrastructure:
Cloud-Native Technologies: The Bank leverages cloud-native technologies and services (e.g., AWS, Azure) for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective infrastructure.
Monitoring and Observability: DevOps teams utilize monitoring and observability tools (e.g., Prometheus, Grafana) to track the performance, availability, and health of microservices in real-time.
Scenario 2: Corporate Banking Platform Transformation
Objective: The CTO of a large multinational bank seeks to transform its corporate banking platform to better serve large corporate clients and improve operational efficiency.
Team Formation:
Organizational Structure:
Technology Stack:
Process Standardization:
Tooling and Infrastructure:
In both scenarios, banks leverage horizontally aligned DevOps teams centred around microservices to drive innovation, agility, and customer-centricity while ensuring operational excellence and regulatory compliance in a highly competitive banking landscape.
Use this EBook to know how the world’s top legacy migration specialists are leveraging no-code technologies to enable legacy systems integration and automate data streams.
Qualify for a free consultation on the right application modernization strategy for your enterprise.